# baseIntersection
# Description
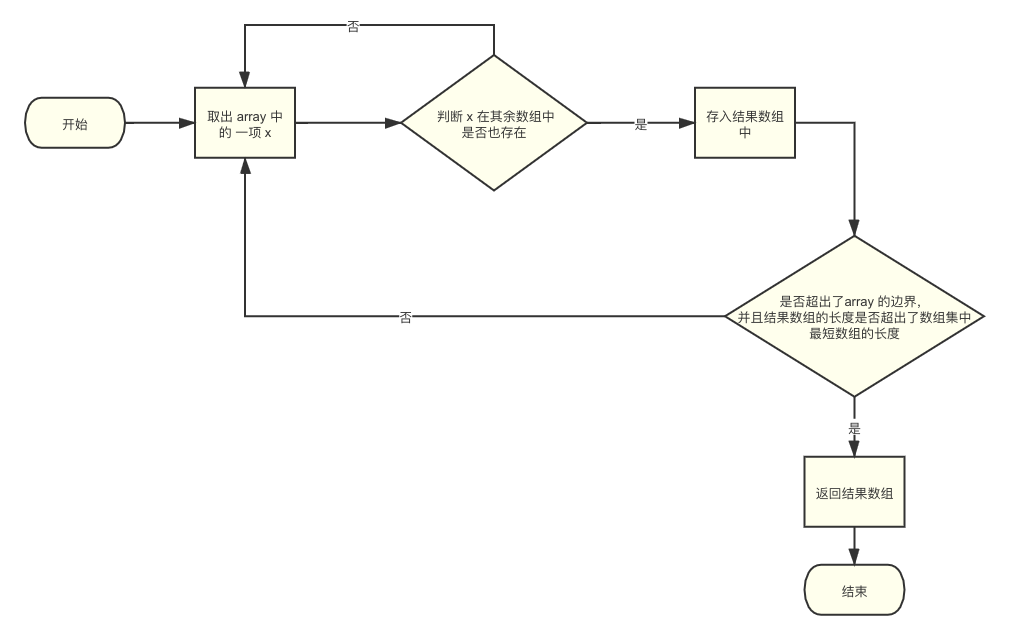
baseIntersection 的作用是找出多个数组之间的交集。
# Params
(arrays, iteratee, comparator)
{Array} arrays - 数组集合(二维数组)
{Function} [iteratee] - 每个元素调用的迭代器。
{Function} [comparator] - 每个元素调用的比较器
# Return
Array
# Depend
import SetCache from './SetCache.js'
import arrayIncludes from './arrayIncludes.js'
import arrayIncludesWith from './arrayIncludesWith.js'
import map from '../map.js'
import cacheHas from './cacheHas.js'
SetCache 源码分析
arrayIncludes 源码分析
arrayIncludesWith 源码分析
map 源码分析
cacheHas 源码分析
# Code
function baseIntersection(arrays, iteratee, comparator) {
const includes = comparator ? arrayIncludesWith : arrayIncludes
const length = arrays[0].length
const othLength = arrays.length
const caches = new Array(othLength)
const result = []
let array
let maxLength = Infinity
let othIndex = othLength
while (othIndex--) {
array = arrays[othIndex]
if (othIndex && iteratee) {
array = map(array, (value) => iteratee(value))
}
maxLength = Math.min(array.length, maxLength)
caches[othIndex] = !comparator && (iteratee || (length >= 120 && array.length >= 120))
? new SetCache(othIndex && array)
: undefined
}
array = arrays[0]
let index = -1
const seen = caches[0]
outer:
while (++index < length && result.length < maxLength) {
let value = array[index]
const computed = iteratee ? iteratee(value) : value
value = (comparator || value !== 0) ? value : 0
if (!(seen
? cacheHas(seen, computed)
: includes(result, computed, comparator)
)) {
othIndex = othLength
while (--othIndex) {
const cache = caches[othIndex]
if (!(cache
? cacheHas(cache, computed)
: includes(arrays[othIndex], computed, comparator))
) {
continue outer
}
}
if (seen) {
seen.push(computed)
}
result.push(value)
}
}
return result
}
# Analyze
# 交集
确定结果数组的长度。最终的结果数组长度肯定不会超过数组集中最短的数组长度。
maxLength = Math.min(array.length, maxLength)lodash 思路是遍历数组集第一项(下标为0),如果第一个数组中的值,在剩余的每个数组中都存在,那就可以将它 push 到结果数组中,如果第一个数组中,有值在其他任一数组中不存在,则证明不是交集需要的值
while (--othIndex) {
const cache = caches[othIndex]
if (!(cache
? cacheHas(cache, computed)
: includes(arrays[othIndex], computed, comparator))
) {
continue outer
}
}
# 取结果数组长度
const othLength = arrays.length
const result = []
let array
let maxLength = Infinity
let othIndex = othLength
while (othIndex--) {
maxLength = Math.min(array.length, maxLength)
}
首先获取到 整个
arrays数组集的length,定义结果数组result定义
maxLength为Infinity, 暂存othLength为othIndex,做 递减使用while循环遍历,每次都会更新maxLength为最小值在最终
while循环时,会根据maxLength作为结束条件判断
# iteratee
iteratee 函数是用来处理值的,比如将字符串数字或者 boolean 转为数字等,对数组的每个元素都会调用
while (othIndex--) {
array = arrays[othIndex]
if (othIndex && iteratee) {
array = map(array, (value) => iteratee(value))
}
maxLength = Math.min(array.length, maxLength)
caches[othIndex] = !comparator && (iteratee || (length >= 120 && array.length >= 120))
? new SetCache(othIndex && array)
: undefined
}
const computed = iteratee ? iteratee(value) : value
othIndex就是根据arrays.length来的,所以这里取值,获取数组集每一项如果
othIndex不为 0,并且传入了iteratee函数,则针对于获取到的数组每一项进行map迭代,使用iteratee函数处理每一项的值这里并没有处理 数组集第一项,是因为最终遍历时,要通过第一项的值来判断,第一项值的处理放到了最终的while循环中
# comparator
const includes = comparator ? arrayIncludesWith : arrayIncludes
可以看到 comparator 的作用主要是用来进行比较使用的,比如正常逻辑用 === , 在传入了 comparator 后,可以自定义比较啊, 比如 自定义为 ==
# cache
const caches = new Array(othLength)
caches[othIndex] = !comparator && (iteratee || (length >= 120 && array.length >= 120))
? new SetCache(othIndex && array)
: undefined
这里也是在获取结果数组长度的 while 循环中设置的,要么设置为 new SetCache 要么为 undefined,满足以下条件会将遍历的当前项设置为 new SetCache (这里数组集第一项如果满足条件会初始化为一个空的 SetCache,没有数据)
- 用户没有传入 comparator
- 传入了 iteratee 或者
- 数组集第一项的 length >= 120 并且 当前遍历的数组 length >= 120
到现在为止,已经处理了结果数组的最大长度,处理了数组集中除第一项之外其他的迭代函数(iteratee),处理了缓存(caches),下面开始分析代码实现过程
第一步
- 定义了
includes函数采用默认对比还是用户自定对比(comparator) - 拿到数组第一项的长度(
arrays[0].length) 和 数组集中的数组个数(arrays.length) - 定义了缓存的数组长度(
new Array(othLength)) - 定义了结果数组
result
- 定义了
第二步
- 定义了
array变量暂存,定义了结果数组的最大长度,缓存了arrays.length的长度(othIndex) while循环遍历- 循环开始,首先拿到当前遍历下标所对应的 数组集中的数组
- 如果在当前遍历下标不为0,并且用户自定义了迭代函数(
iteratee)的情况下,对于当前下标对应的数组集中的数组做map遍历,对于每一项值调用iteratee函数进行处理 - 重新赋值
maxLength,在while循环中 一直取 最小值(Math.min)- 这里其实可以加一个判断遍历的数组
length是否大于0,如果为0,可以直接break掉循环,并返回空数组
- 这里其实可以加一个判断遍历的数组
- 针对是否缓存数组做一个处理,如果需要则设置为
SetCache否则为undefined
- 定义了
第三步
- 重新定义
array变量为数组第一项,去缓存(cache)第一项的值,赋值给seen,定义下标index为-1 - 定义外层
while循环label为outer,结束条件为++index < length && result.length < maxLength- 也就是
index小于数组集第一项的长度,并且 结果数组的长度 小于 最大长度
- 也就是
- 循环开始,拿到
array(数组集第一项) 对应下标的值value,并且定义computed变量用作缓存value值 - 如果 用户自定义了
iteratee函数,则使用iteratee函数处理value值,赋值给computed,否则computed就为value - 紧接着处理
value值,会将+0和-0都会处理为0 - 开始
if判断,判断条件为!(seen ? cacheHas(seen, computed) : includes(result, computed, comparator))- 判断
seen(caches第一项,和数组集第一项对应) 是否为undefined - 如果不是
undefined,则seen为SetCache,使用cacheHas判断seen中是否已经存在当前计算后(computed)的值 - 如果是
undefined, 就使用includes判断 结果数组中,是否已经存在当前计算后的值(computed) - 如果传入了
comparator这里判断方法调用的就是arrayIncludesWith, 否则默认调用arrayIncludes - 根据 三目运算符 返回的结果,取非,也就是如果当前计算后的值,不存在于结果数组的情况下,才会进入 if 代码块
- 判断
- 进入
if代码块后,开始遍历整个数组集,内层while循环 - 同样也是 缓存了 数组集的长度
othLength为othIndex,做while递减使用 while循环中 也是有一个if判断,判断条件为!(cache ? cacheHas(cache, computed) : includes(arrays[othIndex], computed, comparator))- 从缓存中取当前遍历的数组缓存,判断是否为
undefined - 如果不为
undefined,使用cacheHas判断当前cache中是否有computed - 如果为
undefined,则使用includes进行判断 - 也就是,如果当前遍历的数组中,不存在
computed的值,才会进入代码块
- 从缓存中取当前遍历的数组缓存,判断是否为
- 进入代码块后,会
continue掉当前外层循环,也就是说,正在判断的array(数组集第一项) 中的值,在其他数组中必须存在,如有一个数组不存在当前进行判断的值,则就跳出这次循环,进而判断下一个值 - 如果整个 内层
while循环完成后,都没有continue掉,则证明这个 值,就是要的交集结果中的一个 - 判断如果
seen为SetCache,seen.push(computed),用作下一次判断 - 结果数组
result.push(value)
- 重新定义
最后,整个循环遍历结束后,返回结果数组
# Remark
数组取交集,lodash 的思路十分的简单,你有多个数组,我只取第一个,根据第一个的值来进行判断,如果第一个数组中的一些值,在其他数组中都存在,那这些值就是你要的交集。这个意思就相当于说,交集的值,在第一个数组中肯定存在,如果在第一个数组中不存在,那肯定不是交集,所以我们只需要循环第一个数组的值来进行判断即可达到我们取交集的目的。
同时的,结果数组的长度,肯定取整个数组集中长度最短的那个
# Example
const arrs = [
[1,2,3,4,5],
[2,3,4,5,6],
[3,4,5,6,7],
[4,5,6,7,8]
]
baseIntersection(arrs) // [ 4, 5 ]